Impact of Glycosylation on the Local Backbone Flexibility of Well-Defined IgG1-Fc Glycoforms Using Hydrogen Exchange-Mass Spectrometry (HX-MS)
Abstract
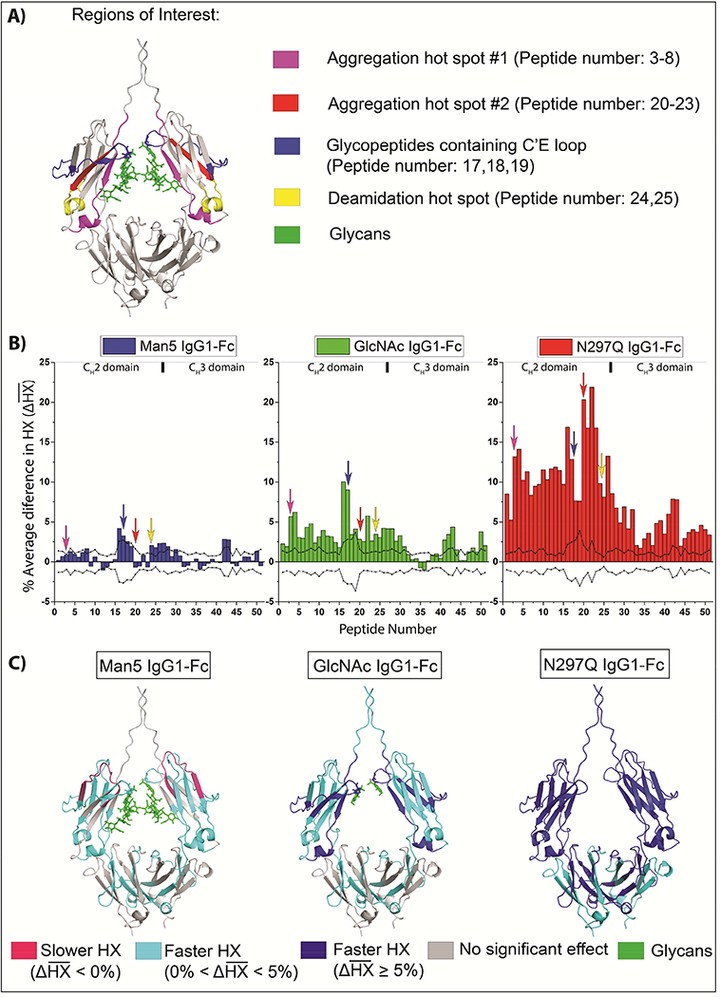
We have utilized hydrogen exchange-mass spectrometry (HX-MS) to characterize local backbone flexibility of four well-defined IgG1-Fc glycoforms expressed and purified from Pichia pastoris, two of which were prepared using subsequent in vitro enzymatic treatments. Progressively decreasing the size of the N-linked N297 oligosaccharide from high mannose (Man8-Man12), to Man5, to GlcNAc, to non-glycosylated N297Q resulted in progressive increases in backbone flexibility. Comparison of these results with recently published physicochemical stability and Fcγ receptor binding data with the same set of glycoproteins provide improved insights into correlations between glycan structure and these pharmaceutical properties. Flexibility significantly increased upon glycan truncation in two potential aggregation prone regions. In addition, a correlation was established between increased local backbone flexibility and increased deamidation at asparagine 315. Interestingly, the opposite trend was observed for oxidation of tryptophan 277 where faster oxidation correlated with decreased local backbone flexibility. Finally, a trend of increasing C’E glycopeptide loop flexibility with decreasing glycan size was observed that correlates with their FcγRIIIa receptor binding properties. These well-defined IgG1-Fc glycoforms serve as a useful model system to identify physicochemical stability and local backbone flexibility data sets potentially discriminating between various IgG glycoforms for potential applicability to future comparability or biosimilarity assessments.